Firing temperature
Curing or firing a porcelain enameling coating is done in high temperature furnaces.
Firing temperatures may range between 500 and 900 degrees Celsius, depening upon the substrate & frit type.
Furnace insulation
In the early days these furnaces were made of refractory bricks.
However, such bricks are sensitive for thermal shocks and need to be heated up & cooled down very slowly.
Therefore modern enameling furnaces are nowadays made of Low Thermal Mass insulation materials, like stone wool, vermiculite & ceramic fibers.
The possibility to switch off a LTM furnace at the end of the day and heat it up again within 1 hour the next morning may provide significant annual energy savings upto 75 % in comparison with the old brick-lined furnaces.
Furnace heating
Enameling furnaces are heated by either electricity, gas or light oil.
Gas and oil are usually combusted inside so-called radiant tubes to avoid that the enamel coating and the furnace interior is affected by the resulting combustion gasses, such as CO2 and H2O. (More about furnace atmosphere)
Depending upon the furnace design, combustion exhaust gasses are either evacuated thru the furnace roof or thru a steel or ceramic exhaust gas channel to the furnace preheating zone in order to increase the furnace efficiency.
The remaining energy of the combustion gases may be used for secondary processes, such as heating dryers or the factory hall.
Furnace concepts
There is a wide variety of furnace designs, which may be classified into three groups: box, intermittent & continuous furnaces.
Box furnaces are typically used for small production volumes and/or products with extreme dimensions.
However, most enameling furnaces are equipped with an overhead conveyor, which is runs either continuous or intermittent.
In some case furnaces with intermittent operated conveyors have automatic doors in order to avoid heat losses.
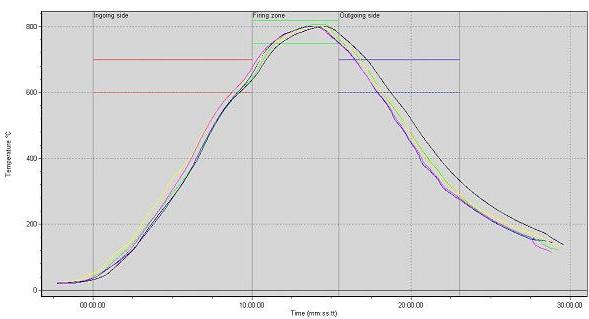
Temperature profiling
Enamels fuse and create a strong bond with the metal substrate when remaining for some minutes above its soaking temperature.
The exact holding time and soaking temperature depends upon the chemical composition of the enamel frit combination.
The primary function of an enameling furnace is to heat-up products to the soaking temperature and ensure that this temperature is maintained for at least the required holding time.
To ensure a good & repeatable enamel coating quality, it is important that the furnace’s Bozsin-box curves are smooth (to avoid thermal shocks) and show little temperature difference between the top & bottom of the products (to avoid color differences and/or wrapping).
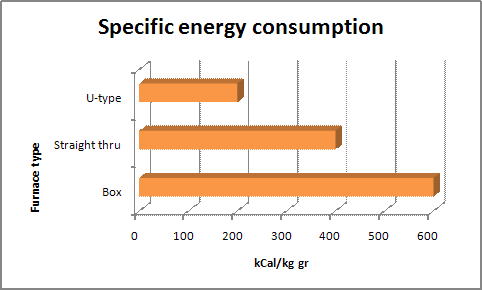
Energy consumption
From an economical point of view, it is important that the furnace requires as little as possible energy to fire a product.
This is called the typical energy consumption of the furnace and is usually expressed as Kcal/kg or KWh/kg.
The typical energy consumption is determined by :
- furnace design
- heating efficiency
- utilization
Energy recovery
Gas or light oil fired furnaces are usually equipped with an internal and/or external heat exchanger to recover excess energy from the furnace exhaust gas in order to improve its heating efficiency.
The investment in an external heat exchanger only pays back, if there are other energy demanding processes near the furnace location.
Furnace conveyors
The furnace conveyor may differ from one enameling plant to the other, because its firing tools may depend on the specific product & production requirement.
Benefit from our experience

The author joined Ferro Holland Engineering Division in 1984 and is since then involved in the design, installation, start-up, optimizing and troubleshooting of industrial enameling furnaces.
Collects temperature profiles, energy consumption & performance data of industrial enameling furnaces since the 80’s.
Helping enamellers to improve the performance of their enameling furnace, based on unique insights from practical experience & fundamental research.